DIAMOND EDUCATION
Every diamond has distinguishable characteristics making it unique just like our fingerprint. A diamond grading system enables us to understand the various attributes and factors which differentiate each piece as well as decide its value. The 4 C’s namely cut, carat, clarity, and color are the defining aspects of all diamonds around the world. The GIA (Gemological Institute of America) established this system in 1953, which soon became a universal language to communicate about diamonds.

About Riddhi Corporation

-
Established :2014
-
Location :Surat, Gujarat, India
-
President :Mr. Patel
-
Workforce :More than 280
-
Sectors :Importer Manufacturer Exporters
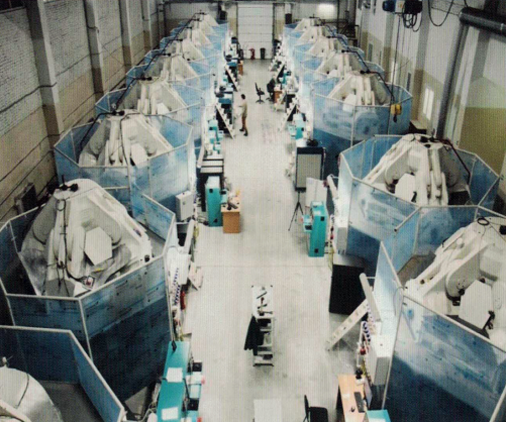
RIDDHI CORPORATION company was founded for growing the largest high-quality single-crystal diamonds of Ila and lb types. We actively develop Jewelry, Industrial and Scientific international market sectors and explore innovative approaches and technologies to improve quality of our diamond products. The company is focused on building partnerships with international research institutes and organizations to create mutually-beneficial collaboration with the main purpose-to contrbute the whole diamond market.
Diamonds production technologies:
HPHT (High Pressure High Temperature) N CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition/ are fundamental methods of diamonds growth.
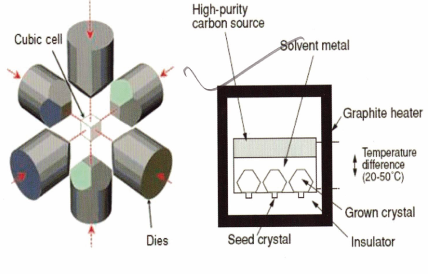
HPHT
High Pressure High Temperature
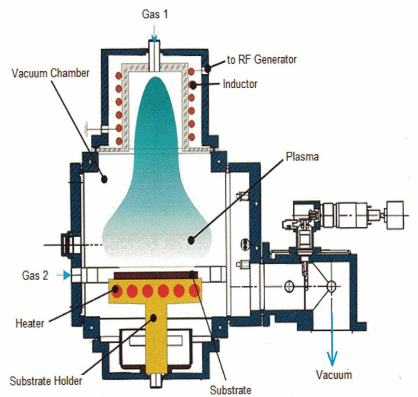
CVD
Chemical Vapor Deposition




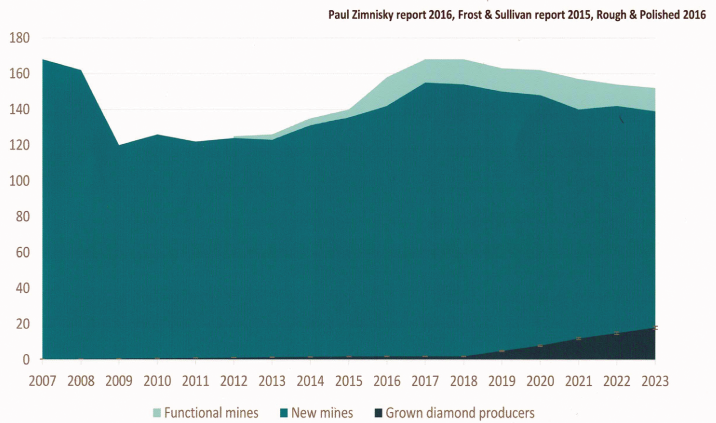
| Si | 4H-SiC | GaN(epi) | Diamond | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Band rap Eg (eV) | 1,12 | 3,23 | 3,44 | 5,5 |
| Electron concentration ni, (cm-3) | 1,15 * 10-10 | 8,2 * 10-9 | 1,9 * 10-10 | 1,6 * 10-27 |
| Dielectric conrant e, | 11,9 | 9,8 | 9 | 5,0 |
| Critical field E MV/Vs | 0,3 | 2,2 | 2,0 | 5,0 |
| Electron mobility u, mc2/Vs | 1350 | 900 | 1150 | 4500 |
| Electron mobility u, mc2/Vs | 480 | 120 | 200 | 3800 |
| Saturated velocity vs, 107cm/s | 1,0 | 2,0 | 3,0 | 2,7 |
| Thermal conductivity Y, W/cmK | 1,5 | 5 | 2 | 22 |
| Max. operationg Temperature Tmax (C) | 175 | 500 | 650 | 900 |
| Breakdown Electric Field (Ebr, MV/cm) | 0,3 | 3 | 3,3 | 10 |
- Micro and power electronics;
- Semiconductors, radio-electronics industry;
- Detectors and sensors;
- Optics & Lasers;
- Vacuum and diamond windows;
- X-ray and medical equipment;
- Quantum computers and photonics;
- Acoustics and electrochemistry;
- Abrasive and drilling materials;
- Aerospace and military fields;
- Processing and manufacturing;
- CVD process;
- Jewelry.
| Location | Presses Type | Presses Amount | Rough volume, ct/month | Rough size, ct | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CJSC FOT | Moscow | BARS-300 | 62 | < 600 | < 6.2 |
| FSBI TISNCM | Troitsk | Toroids | 60 | < 500 | 4.0 - 5.0 |
| V.S.Sobolev IGM SB RAS | Novasibirsk | BARS - 300 | 10 | < 150 | < 6.0 |
| New Diamond technology LLC | Siant Peterburg | Cubic Presses 750 N 850, Toroids | 45 (32/13) | < 4 200 | < 50.00 |






| manufactory standard | Upon special request | |
|---|---|---|
| Size, mm | 2.5 * 2.5 - 10.0 * 10.0 | < 15.0 * 15.0 |
| Thickness, mm | 0.5 | 0.1 - 3.00 |
| Type | lla | llb |
| Face surface oriantation | (110) | (111), (110), (113) |
| Crystallography | Multi-Sectorial | Mono-Sectorial |
| Roughness, nm | 0.1 - 10.0 | - |
| Miscut | 90+/-3o | - |
| Parallelism | +/-0.02 | - |
| Lateral Tolerance, mm | +/-0.05 | - |
| Thicness Tolerance, mm | +/-0.05 | - |
| Edges | Polished | Laser cut |
| Edges Features, mm | <0.02 | |
| Laser | water-jet | |
| Boron concentration, ppb | ~ 10 | < 50ppm |
| Nitrogen concentration, ppb | ~ 10 | < 10ppm |
| Dislocation density, cm-2 | ~ 10 2-3 | < 102 |
| Thermal conductivity, W/mK | ~ 2200 | |
| Absorption coefficient, cm-1 | ~ 0.0045 |
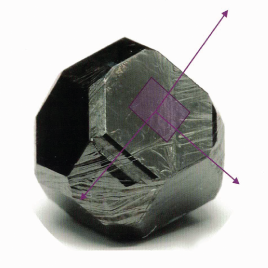
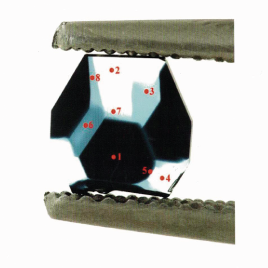
- To produce unique combined (hybrid of lla and lla types) single-crystal diamond plated with different concentrations (e.g. with baron doping);
- To produce substrates for CVD with special angles to enlarge growing diamond;
- To control and manage a growing diamond morphology which allows to make sectors larger;
- To reach low dislocations density approx. 102-3 cm-2 ( in comparison with other suppliers- 107-10 cm-2)
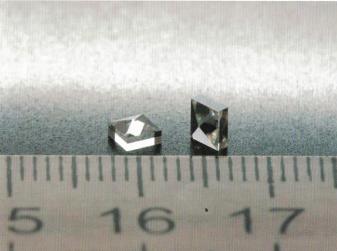

| Diameter, mm | Height, mm | Gridle, mm | Weight, Ct | Cone |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.60 | 2.70 | 1.40 | 0.018 - 0.19 | 45 |
| 3.20 | 3.00 | 1.40 | 0.28 - 0.29 | 45 |
| 3.65 | 3.22 | 1.40 | 0.38 - 0.40 | 45 |
| 4.15 | 3.50 | 1.40 | 0.50 - 0.55 | 45 |
| 4.15 | 3.65 | 2.20 | 0.55 - 0.58 | 35 |
| 4.65 | 3.63 | 2.30 | 0.60 - 0.65 | 30 |





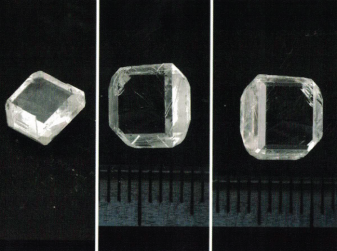
Clarity: IF-SI
Size: 1.0-10.0 Ct+